
In order to be neutral, an atom must have the same number of electrons and protons.
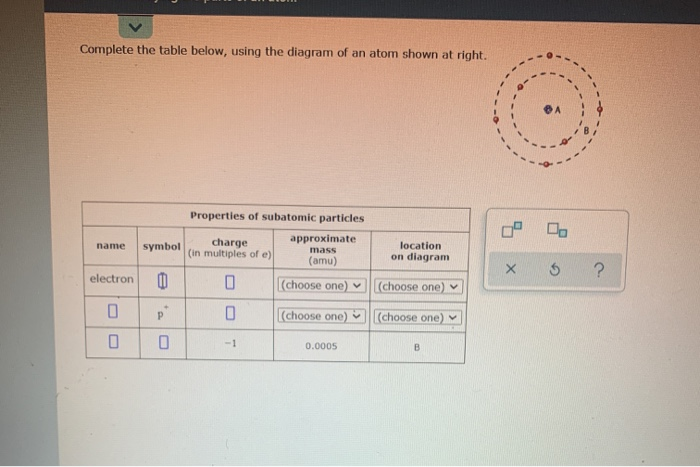
If a neutral atom has 10 protons, it must have 10 electrons. If a neutral atom has 2 protons, it must have 2 electrons. Particles currently thought to be elementary include electrons, the fundamental fermions (quarks, leptons, antiquarks, and antileptons, which generally are matter particles and antimatter particles), as well as the fundamental bosons (gauge bosons and the Higgs. If a neutral atom has 1 proton, it must have 1 electron. In particle physics, an elementary particle or fundamental particle is a subatomic particle that is not composed of other particles. Some properties of these subatomic particles are summarized in Table 1.8. Protons have a positive charge and are located in the of the atom. The process of chemical reactions involves an atom losing or gaining. A gold atom gets its properties from the tiny subatomic particles its made up of. Electrons are negatively charged subatomic.
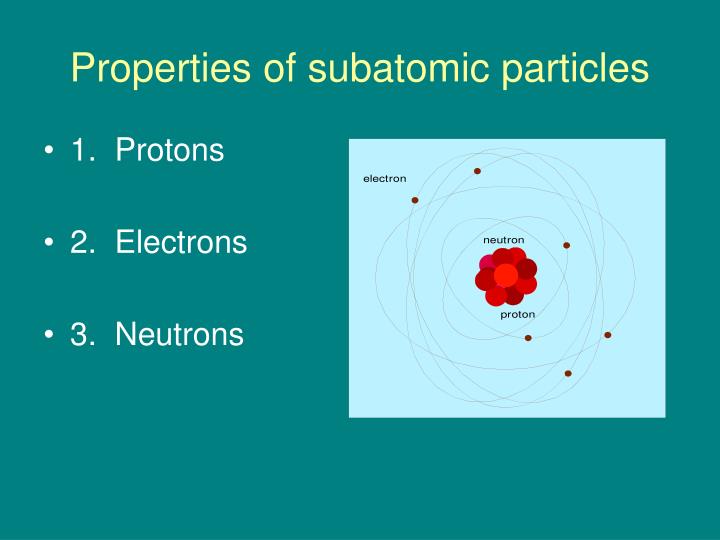
A few points detailing the discovery and the properties of electrons are listed below. Electrons of different atoms come together to participate in chemical bonding. Ions can be formed either by the loss or gain of electrons. In other words, a neutral atom must have exactly one electron for every proton. Atoms are made up of three basic particles, the proton, neutron and the. Atoms contain subatomic particles known as electrons that revolve around the nucleus. Electrons are subatomic particles that revolve around the nucleus of an atom. This means that the negative charge on an electron perfectly balances the positive charge on the proton. Negative and positive charges of equal magnitude cancel each other out.

Since silicon, Si, has an atomic number of 14, every silicon atom contains 14 protons and 14 electrons. A gold atom gets its properties from the tiny subatomic particles it's made up of.Relative charges of 1 and +1 are assigned to the electron and proton, respectively.

Furthermore, since an atom must have an overall neutral charge, the number of protons and electrons found within an atom of an element must be equal. Some properties of these subatomic particles are summarized in Table 1.8.1, which illustrates three important points: Electrons and protons have electrical charges that are identical in magnitude but opposite in sign.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
